| Discrete Dynamics Lab |
The beehive rule
Further details and results relating to the paper:
Wuensche,A.,"Glider dynamics in 3-value hexagonal cellular automata: the beehive rule",
Int. Journ. of Unconventional Computing, Vol.1, No.4, 2005, 375-398.
Preprint available
HERE
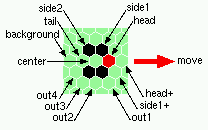
the neighborhood, mutatinons and basic glider
|
The beehive rule-table (kcode) showing all 56 possible mutations, and neighborhoods controling the basic glider 0022000220022001122200021210 (rule v3k6x1.vco in DDLab) | |
\begin{verbatim}
kcode = 0022000220022001122200021210
kcode index
/ totals: 2s+1s+0s=k=6
/ / kcode
basic / / /
glider / / / mutations
--------- / 2_1_0 / 2___1___0
background-> 0: 0 0 6 -> 0 o c -
head+-> 1: 0 1 5 -> 1 0 - 0
2: 0 2 4 -> 2 - Sg cg
3: 0 3 3 -> 1 -+ G - G
out4 4: 0 4 2 -> 2 -+ - G G
out3 5: 0 5 1 -> 0 -+ G G -
out1 6: 0 6 0 -> 0 -+ G G -
side2-> 7: 1 0 5 -> 0 c c -
side1-> 8: 1 1 4 -> 2 - c c
side1+ 9: 1 2 3 -> 2 - cg G
10: 1 3 2 -> 2 -+ - G G
out2 11: 1 4 1 -> 1 -+ G - G
tail 12: 1 5 0 -> 1 -+ G - G
head-> 13: 2 0 4 -> 0 c c -
14: 2 1 3 -> 0 Gs c -
15: 2 2 2 -> 2 - gc gc
16: 2 3 1 -> 2 -+ - G G
17: 2 4 0 -> 0 -+ G G -
18: 3 0 3 -> 0 g c -
19: 3 1 2 -> 2 - c cg
20: 3 2 1 -> 2 - cg Gd
21: 3 3 0 -> 0 -+ G G -
22: 4 0 2 -> 0 G c -
center-> 23: 4 1 1 -> 0 g cg -
24: 4 2 0 -> 2 - cg G
25: 5 0 1 -> 2 - cg G
26: 5 1 0 -> 0 g gc -
27: 6 0 0 -> 0 G Gd -
key to mutations:
quasi-neutral G=25/56, wildcards -+ 10/28
G/g=gliders, G=same/similar dynamics,
g=weak/different, S=spirals, d=dense,
s=sparse, c=chaos, o=order, 0=all 0s
| |
| |
 > >

| |
| 21 types of glider collisions | collision diagrams | |||
no type no before after
head-on odd: 4 2->0 3 6 0
2->2 1 2 2
head-on odd: 4 2->0 3 6 0
2->2 1 2 2
oblige head-on: 8 2->0 3 6 0
2->1 2 4 2
2->4 1 2 4
2->5 1 2 5
2->6 1 2 6
oblique tail-on: 5 2->0 1 2 0
2->1 2 4 2
2->2 1 2 2
2->6 1 2 6
-----------------------------------
totals: 21 21 42 31
gliders
type no before after
self-destruction: 2->0 10 20 0
one-survivor:.... 2->1 4 8 4
conservation:.... 2->2 3 6 6
self-reproduction: 2->4 1 2 4
2->5 1 2 5
2->6 2 4 12
------------
totals 21 42 31
oblique 60 degree head-on collisions - 8 types | 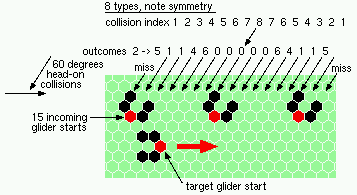
oblique 120 degree tail-on collisions - 5 types | 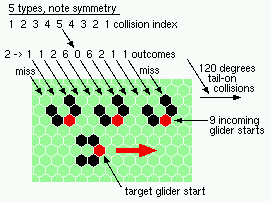
180 degree 0dd head-on collisions - 4 types | 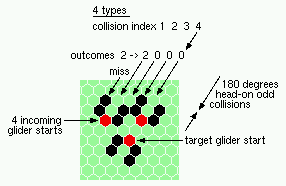
180 even head-on collisions - 4 types | 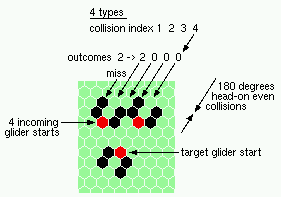
|
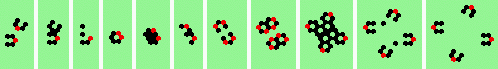
| 8 60degree (head-on oblique) collisions | |
| 1a 2->5 |
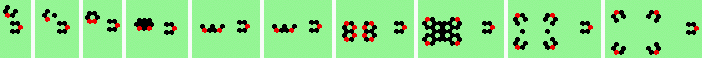
|
| 2a 2->1 |
|
| 3a 2->1 |
|
| 4a 2->4 |
|
| 5a 2->6 |
|
| 6a 2->0 |
|
| 7a 2->0 |
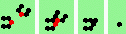
|
| 8a 2->0 |
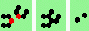
|
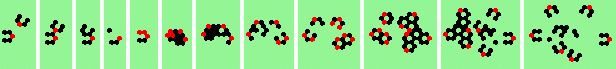
| 5 120degree (oblique tail-on) collisions | |
| 1b tail 2->1 |
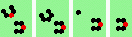
|
| 2b tail 2->1 |
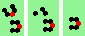
|
| 3b tail 2->2 |
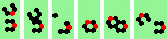 note bounce note bounce
|
| 4b 2->6 |
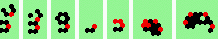 continues as 5a continues as 5a
|
| 5b 2->0 |
|
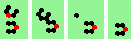
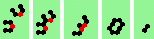
| 4 180degree (head-on) collisions, odd | |
| 1h-odd 2->2 |
|
| 2h-odd 2->0 |

|
| 3h-odd 2->0 |
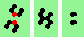
|
| 4h-odd 2->0 |
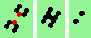
|
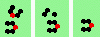
| 4 180 (head-on) collisions, even | |
| 1h-even 2->2 |
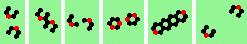
|
| 2h-even 2->0 |
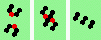
|
| 3h-even 2->0 |
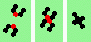
|
| 4h-even 2->0 |
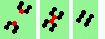
|
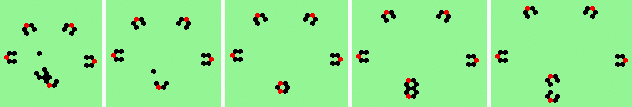
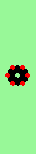
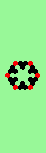
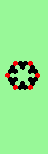
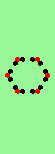
| Exploding red cell makes 6 new gliders | |
| single red->6 |
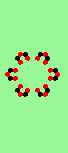
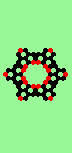
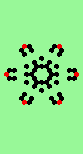
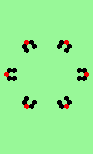
|
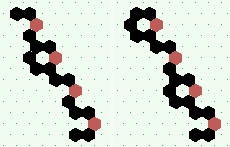
| polymer-like gliders made up from sub-units | |
| p=1 |
 .. ..
|
| p=2 |
 .. ..
 .. ..
 .. ..
|
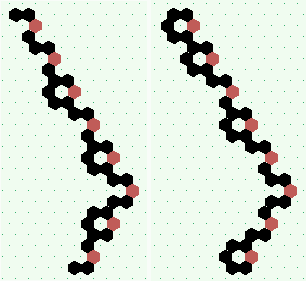
| p=2 |
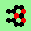 .. ..
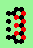
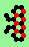
|
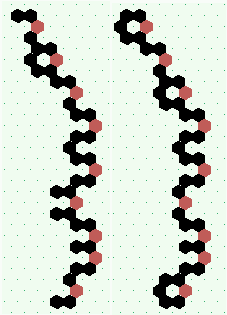
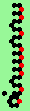
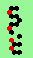
| p=4 |
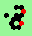
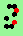
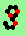
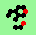 .. ..
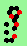

|
| p=4 |
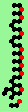
|
| p=4 |
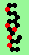

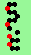
|
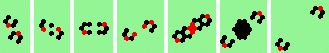
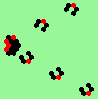
| glider-guns (puffer-trains) with various periods shooting 1 to 4 glider streams | |
| 1a streams=1 period=4 | 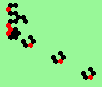
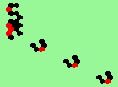
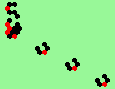
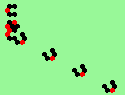
|
| 1b streams=1 period=4 | 
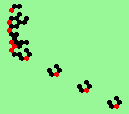
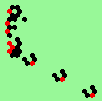
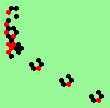
|
| 1c streams=1 period=4 | 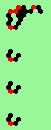
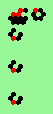
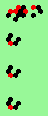
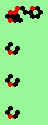
|
| 2a streams=2 period=4 |
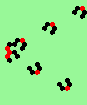

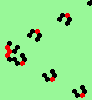
|
| 2b streams=2 period=4 |
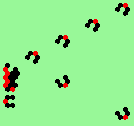
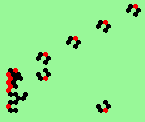


|
| 2c streams=2 period=4 |
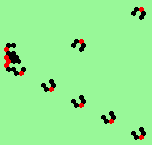
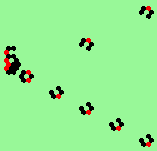
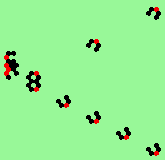
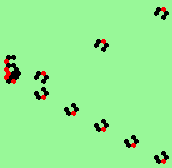
|
| 2d streams=2 period=4 |
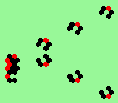
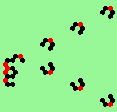

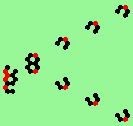
|
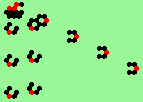
| 3a streams=3 period=4 |


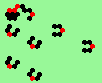
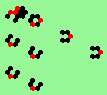
|
| 3b streams=3 period=4 |




|
| 3c streams=3 period=4 |
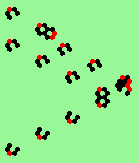
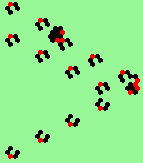
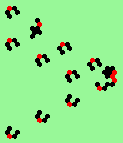
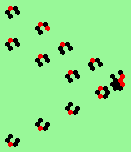
|
| 3d streams=3 period=4 |
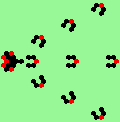
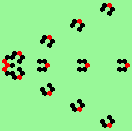
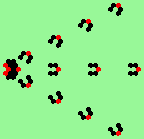
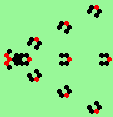
|
| 3e streams=3 period=4 |
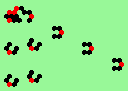
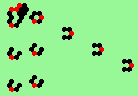
|
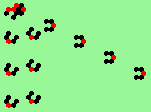
| 4a streams=4 period=8 |





|
|
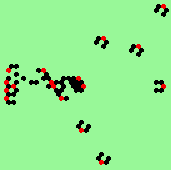
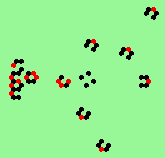
Static glider-gun: period=13, multiple streams in 6 directions (found behind puffer-train) |
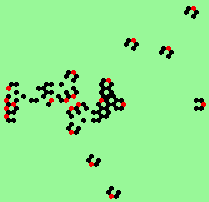
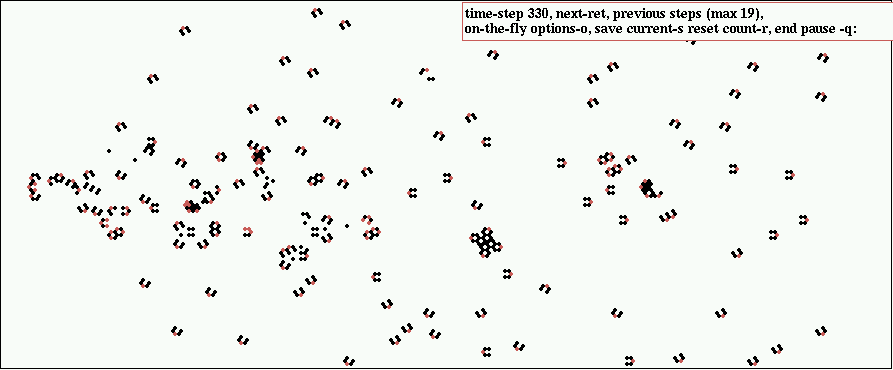
Puffer-train: moving west, absorbing boundary conditions, 222x122 click to enlarge |

|
|
| 2 interesting mutations | |
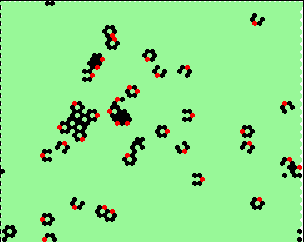 index 23: 4 1 1 -> 0 changed to 2 |
 index 2: 0 2 4 -> 2 changed to 1 |
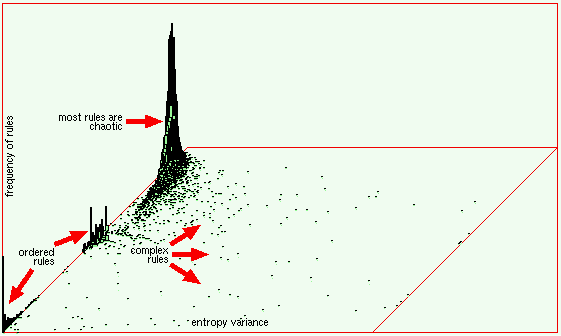
| Classifying rule-space to find v=3 k=6 complex rules | |
|
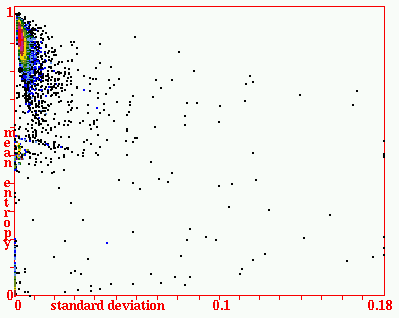
|
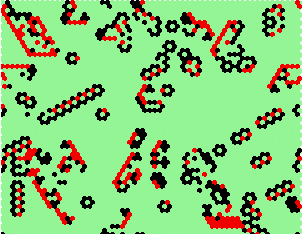
| Examples of other complex-rules | ||
 kcode=2200021000222201110201212210 0=10 2=11 1=7 |
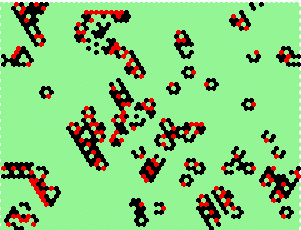
 kcode=0222200220000200100201102110 0=14 2=9 1=5 |
 kcode=0220002120022202120200112110 0=11 2=11 1=6 |
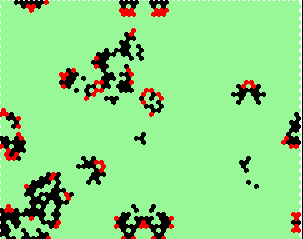
 kcode= 0200001120100200002200120110 0=15 2=6 1=6 |
 kcode= 0200202022222200012100002100 0=14 2=9 1=3 |
 kcode=0122120102200122010000102000 0=14 2=8 1=6 |